RPACT Survival Designs
November 19, 2024
RPACT Survival Designs

The Situation
Assume we want to design a two-arm group sequential trial with a time to event endpoint where the summary measure of interest is the hazard ratio \(\omega\)
Suppose we wish to test
\[ H_0: \omega \geq 1 \text{ against } H_1: \omega < 1 \]
We require:
- \(\alpha = 0.025\)
- Power \(1 - \beta = 0.8\) at \(\omega = 0.6\)
- Allocation ratio 1 : 1
Required Number of Events
Question 1
How many events would be required for a fixed sample size design?
Sample size calculation for a survival endpoint
Fixed sample analysis, one-sided significance level 2.5%, power 80%. The results were calculated for a two-sample logrank test, H0: hazard ratio = 1, H1: hazard ratio = 0.6, control pi(2) = 0.2, event time = 12, accrual time = 12, accrual intensity = 62.1, follow-up time = 6.
| Stage | Fixed |
|---|---|
| Stage level (one-sided) | 0.0250 |
| Efficacy boundary (z-value scale) | 1.960 |
| Efficacy boundary (t) | 0.700 |
| Number of subjects | 745.0 |
| Number of events | 120.3 |
| Analysis time | 18.00 |
| Expected study duration under H1 | 18.00 |
Legend:
- (t): treatment effect scale
Required Number Of Subjects
Obviously, some default parameters were used to derive the required number of subjects
Design plan parameters and output for survival data
Design parameters
- Critical values: 1.960
- Significance level: 0.0250
- Type II error rate: 0.2000
- Test: one-sided
User defined parameters
- Hazard ratio: 0.600
Default parameters
- Theta H0: 1
- Type of computation: Schoenfeld
- Assumed control rate: 0.200
- Planned allocation ratio: 1
- Event time: 12
- Accrual time: 12.00
- kappa: 1
- Follow up time: 6.00
- Drop-out rate (1): 0.000
- Drop-out rate (2): 0.000
- Drop-out time: 12.00
Sample size and output
- Direction upper: FALSE
- Assumed treatment rate: 0.125
- median(1): 62.1
- median(2): 37.3
- lambda(1): 0.0112
- lambda(2): 0.0186
- Number of events: 120.3
- Accrual intensity: 62.1
- Number of events fixed: 120.3
- Number of subjects fixed: 745
- Number of subjects fixed (1): 372.5
- Number of subjects fixed (2): 372.5
- Analysis time: 18.00
- Study duration: 18.00
- Critical values (treatment effect scale): 0.700
Legend
- (i): values of treatment arm i
Required Number Of Subjects
For the survival time distributions, we assume:
- Median survival on the control arm is 1 year.
- Exponential survival distribution.
Question 2
What is the sample size (number of subjects) for a fixed sample size design if the recruitment lasts 3 years and the (additional) follow-up time lasts 2 years, i.e., it is planned to conduct the study in 5 years?
Required Number Of Subjects
Sample size calculation for a survival endpoint
Fixed sample analysis, one-sided significance level 2.5%, power 80%. The results were calculated for a two-sample logrank test, H0: hazard ratio = 1, H1: hazard ratio = 0.6, control median(2) = 1, accrual time = 3, accrual intensity = 48.7, follow-up time = 2.
| Stage | Fixed |
|---|---|
| Stage level (one-sided) | 0.0250 |
| Efficacy boundary (z-value scale) | 1.960 |
| Efficacy boundary (t) | 0.700 |
| Number of subjects | 146.2 |
| Number of events | 120.3 |
| Analysis time | 5.00 |
| Expected study duration under H1 | 5.00 |
Legend:
- (t): treatment effect scale
For recruitment assumptions, we assume:
- It is possible to recruit 50 subjects per year at a uniform rate.
- Recruitment lasts 3 years.
- I.e., slightly higher number of available subjects.
Follow-up time needs to be calculated
Question 3
What is the expected study duration for a fixed sample size design?
getSampleSizeSurvival(
alpha = 0.025,
beta = 0.2,
hazardRatio = 0.6,
median2 = 1,
accrualTime = c(0, 3),
accrualIntensity = 50
) |> summary()Sample size calculation for a survival endpoint
Fixed sample analysis, one-sided significance level 2.5%, power 80%. The results were calculated for a two-sample logrank test, H0: hazard ratio = 1, H1: hazard ratio = 0.6, control median(2) = 1, accrual time = 3, accrual intensity = 50.
| Stage | Fixed |
|---|---|
| Stage level (one-sided) | 0.0250 |
| Efficacy boundary (z-value scale) | 1.960 |
| Efficacy boundary (t) | 0.700 |
| Number of subjects | 150.0 |
| Number of events | 120.3 |
| Analysis time | 4.78 |
| Expected study duration under H1 | 4.78 |
Legend:
- (t): treatment effect scale
Question 4
Suppose recruitment lasts 3.5 years instead of 3 years. What would be the expected study duration for a fixed sample size design?
getSampleSizeSurvival(
alpha = 0.025,
beta = 0.2,
hazardRatio = 0.6,
median2 = 1,
accrualTime = c(0, 3.5),
accrualIntensity = 50
) |> summary()Sample size calculation for a survival endpoint
Fixed sample analysis, one-sided significance level 2.5%, power 80%. The results were calculated for a two-sample logrank test, H0: hazard ratio = 1, H1: hazard ratio = 0.6, control median(2) = 1, accrual time = 3.5, accrual intensity = 50.
| Stage | Fixed |
|---|---|
| Stage level (one-sided) | 0.0250 |
| Efficacy boundary (z-value scale) | 1.960 |
| Efficacy boundary (t) | 0.700 |
| Number of subjects | 175.0 |
| Number of events | 120.3 |
| Analysis time | 4.20 |
| Expected study duration under H1 | 4.20 |
Legend:
- (t): treatment effect scale
Adding An Interim Analysis
We wish to add an interim analysis for efficacy. The interim should happen after approximately half the required number of events. An O’Brien-Fleming type alpha-spending function will be used. No futility analysis is considered (for now).
Question 5
Using the same design assumptions as above with a recruitment period of 3.5 years, perform the sample size calculation.
Adding An Interim Analysis
Sample size calculation for a survival endpoint
Sequential analysis with a maximum of 2 looks (group sequential design), one-sided overall significance level 2.5%, power 80%. The results were calculated for a two-sample logrank test, H0: hazard ratio = 1, H1: hazard ratio = 0.6, control median(2) = 1, accrual time = 3.5, accrual intensity = 50.
| Stage | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Planned information rate | 50% | 100% |
| Cumulative alpha spent | 0.0015 | 0.0250 |
| Stage levels (one-sided) | 0.0015 | 0.0245 |
| Efficacy boundary (z-value scale) | 2.963 | 1.969 |
| Efficacy boundary (t) | 0.466 | 0.699 |
| Cumulative power | 0.1641 | 0.8000 |
| Number of subjects | 130.3 | 175.0 |
| Expected number of subjects under H1 | 167.7 | |
| Cumulative number of events | 60.4 | 120.8 |
| Expected number of events under H1 | 110.9 | |
| Analysis time | 2.61 | 4.22 |
| Expected study duration under H1 | 3.95 | |
| Exit probability for efficacy (under H0) | 0.0015 | |
| Exit probability for efficacy (under H1) | 0.1641 |
Legend:
- (t): treatment effect scale
After how many events is the interim and final analysis to take place?
How long would it take to reach the required number of interim and final events according to the design assumptions?
What is the critical value for the hazard ratio at the interim and final analysis?
What is the expected study duration according to the design assumptions (i.e., under the alternative hypothesis)?
What is the expected number of subjects according to the design assumptions (i.e., under the alternative hypothesis)?
What is the expected number of events under the null hypothesis and under the alternative?
getSampleSizeSurvival(
design = design,
hazardRatio = 0.6,
median2 = 1,
accrualTime = c(0, 3.5),
accrualIntensity = 50
) |> print()Design plan parameters and output for survival data
Design parameters
- Information rates: 0.500, 1.000
- Critical values: 2.963, 1.969
- Futility bounds (non-binding): -Inf
- Cumulative alpha spending: 0.001525, 0.025000
- Local one-sided significance levels: 0.001525, 0.024500
- Significance level: 0.0250
- Type II error rate: 0.2000
- Test: one-sided
User defined parameters
- median(2): 1.0
- Hazard ratio: 0.600
- Accrual time: 3.50
- Accrual intensity: 50.0
Default parameters
- Theta H0: 1
- Type of computation: Schoenfeld
- Planned allocation ratio: 1
- kappa: 1
- Drop-out rate (1): 0.000
- Drop-out rate (2): 0.000
- Drop-out time: 12.00
Sample size and output
- Direction upper: FALSE
- median(1): 1.7
- lambda(1): 0.416
- lambda(2): 0.693
- Maximum number of subjects: 175
- Maximum number of subjects (1): 87.5
- Maximum number of subjects (2): 87.5
- Number of subjects [1]: 130.3
- Number of subjects [2]: 175
- Maximum number of events: 120.8
- Follow up time: 0.72
- Reject per stage [1]: 0.1641
- Reject per stage [2]: 0.6359
- Early stop: 0.1641
- Analysis time [1]: 2.61
- Analysis time [2]: 4.22
- Expected study duration: 3.95
- Maximal study duration: 4.22
- Cumulative number of events [1]: 60.4
- Cumulative number of events [2]: 120.8
- Expected number of events under H0: 120.7
- Expected number of events under H0/H1: 119.3
- Expected number of events under H1: 110.9
- Expected number of subjects under H1: 167.7
- Critical values (treatment effect scale) [1]: 0.466
- Critical values (treatment effect scale) [2]: 0.699
Legend
- (i): values of treatment arm i
- [k]: values at stage k
Adding A Futility Boundary
Suppose at the time of the interim analysis we wish to add a futility stopping boundary.
A simple rule is considered: if the Z-statistic is above zero (where negative values of the Z-statistic indicate treatment benefit), then the trial is stopped for futility.
The rule is considered non-binding.
Question 6
Create a design object which includes this futility stopping rule.
- Use the function
getPowerSurvival()to calculate the overall power when adding the futility boundary under the same design assumptions as above. Assume recruitment lasts for 3.5 years (50 subjects per year). Assume that the maximum number of events is 121. What is the the overall power? The expected study duration and number of subjects?
Direction of test statistic
Specify directionUpper = FALSE because power is directed towards hazard ratio < 1
getPowerSurvival(
design = designWithFutility,
hazardRatio = 0.6,
median2 = 1,
directionUpper = FALSE,
maxNumberOfEvents = 121,
accrualTime = c(0, 3.5),
accrualIntensity = 50
) |> summary()Power calculation for a survival endpoint
Sequential analysis with a maximum of 2 looks (group sequential design), one-sided overall significance level 2.5%. The results were calculated for a two-sample logrank test, H0: hazard ratio = 1, power directed towards smaller values, H1: hazard ratio = 0.6, control median(2) = 1, maximum number of events = 121, accrual time = 3.5, accrual intensity = 50.
| Stage | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Planned information rate | 50% | 100% |
| Cumulative alpha spent | 0.0015 | 0.0250 |
| Stage levels (one-sided) | 0.0015 | 0.0245 |
| Efficacy boundary (z-value scale) | 2.963 | 1.969 |
| Futility boundary (z-value scale) | 0 | |
| Efficacy boundary (t) | 0.467 | 0.699 |
| Futility boundary (t) | 1.000 | |
| Cumulative power | 0.1645 | 0.7977 |
| Number of subjects | 130.5 | 175.0 |
| Expected number of subjects under H1 | 166.6 | |
| Cumulative number of events | 60.5 | 121.0 |
| Expected number of events under H1 | 109.6 | |
| Analysis time | 2.61 | 4.22 |
| Expected study duration under H1 | 3.92 | |
| Overall exit probability (under H0) | 0.5015 | |
| Overall exit probability (under H1) | 0.1880 | |
| Exit probability for efficacy (under H0) | 0.0015 | |
| Exit probability for efficacy (under H1) | 0.1645 | |
| Exit probability for futility (under H0) | 0.5000 | |
| Exit probability for futility (under H1) | 0.0235 |
Legend:
- (t): treatment effect scale
- What is the expected study duration and number of subjects under the null hypothesis?
getPowerSurvival(
design = designWithFutility,
hazardRatio = 1,
median2 = 1,
directionUpper = FALSE,
maxNumberOfEvents = 121,
accrualTime = c(0, 3.5),
accrualIntensity = 50
) |> summary()Power calculation for a survival endpoint
Sequential analysis with a maximum of 2 looks (group sequential design), one-sided overall significance level 2.5%. The results were calculated for a two-sample logrank test, H0: hazard ratio = 1, power directed towards smaller values, H1: hazard ratio = 1, control median(2) = 1, maximum number of events = 121, accrual time = 3.5, accrual intensity = 50.
| Stage | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Planned information rate | 50% | 100% |
| Cumulative alpha spent | 0.0015 | 0.0250 |
| Stage levels (one-sided) | 0.0015 | 0.0245 |
| Efficacy boundary (z-value scale) | 2.963 | 1.969 |
| Futility boundary (z-value scale) | 0 | |
| Efficacy boundary (t) | 0.467 | 0.699 |
| Futility boundary (t) | 1.000 | |
| Cumulative power | 0.0015 | 0.0247 |
| Number of subjects | 118.7 | 175.0 |
| Expected number of subjects under H1 | 146.8 | |
| Cumulative number of events | 60.5 | 121.0 |
| Expected number of events under H1 | 90.7 | |
| Analysis time | 2.37 | 3.78 |
| Expected study duration under H1 | 3.08 | |
| Overall exit probability (under H0) | 0.5015 | |
| Overall exit probability (under H1) | 0.5015 | |
| Exit probability for efficacy (under H0) | 0.0015 | |
| Exit probability for efficacy (under H1) | 0.0015 | |
| Exit probability for futility (under H0) | 0.5000 | |
| Exit probability for futility (under H1) | 0.5000 |
Legend:
- (t): treatment effect scale
Together:
getPowerSurvival(
design = designWithFutility,
hazardRatio = c(0.6, 1),
median2 = 1,
directionUpper = FALSE,
maxNumberOfEvents = 121,
accrualTime = c(0, 3.5),
accrualIntensity = 50
) |> summary()Power calculation for a survival endpoint
Sequential analysis with a maximum of 2 looks (group sequential design), one-sided overall significance level 2.5%. The results were calculated for a two-sample logrank test, H0: hazard ratio = 1, power directed towards smaller values, H1: hazard ratio as specified, control median(2) = 1, maximum number of events = 121, accrual time = 3.5, accrual intensity = 50.
| Stage | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Planned information rate | 50% | 100% |
| Cumulative alpha spent | 0.0015 | 0.0250 |
| Stage levels (one-sided) | 0.0015 | 0.0245 |
| Efficacy boundary (z-value scale) | 2.963 | 1.969 |
| Futility boundary (z-value scale) | 0 | |
| Efficacy boundary (t) | 0.467 | 0.699 |
| Futility boundary (t) | 1.000 | |
| Cumulative power, HR = 0.6 | 0.1645 | 0.7977 |
| Cumulative power, HR = 1 | 0.0015 | 0.0247 |
| Number of subjects, HR = 0.6 | 130.5 | 175.0 |
| Number of subjects, HR = 1 | 118.7 | 175.0 |
| Expected number of subjects under H1, HR = 0.6 | 166.6 | |
| Expected number of subjects under H1, HR = 1 | 146.8 | |
| Cumulative number of events | 60.5 | 121.0 |
| Expected number of events under H1, HR = 0.6 | 109.6 | |
| Expected number of events under H1, HR = 1 | 90.7 | |
| Analysis time, HR = 0.6 | 2.61 | 4.22 |
| Analysis time, HR = 1 | 2.37 | 3.78 |
| Expected study duration under H1, HR = 0.6 | 3.92 | |
| Expected study duration under H1, HR = 1 | 3.08 | |
| Overall exit probability (under H0) | 0.5015 | |
| Overall exit probability (under H1) | 0.1880 | |
| Exit probability for efficacy (under H0) | 0.0015 | |
| Exit probability for efficacy (under H1), HR = 0.6 | 0.1645 | |
| Exit probability for efficacy (under H1), HR = 1 | 0.0015 | |
| Exit probability for futility (under H0) | 0.5000 | |
| Exit probability for futility (under H1), HR = 0.6 | 0.0235 | |
| Exit probability for futility (under H1), HR = 1 | 0.5000 |
Legend:
- (t): treatment effect scale
- HR: hazard ratio
Range of Plots
getPowerSurvival(
design = designWithFutility,
hazardRatio = seq(0.6, 1, 0.01),
median2 = 1,
directionUpper = FALSE,
maxNumberOfEvents = 121,
accrualTime = c(0, 3.5),
accrualIntensity = 50
) |> plot(type = "all")$`Boundaries Z Scale`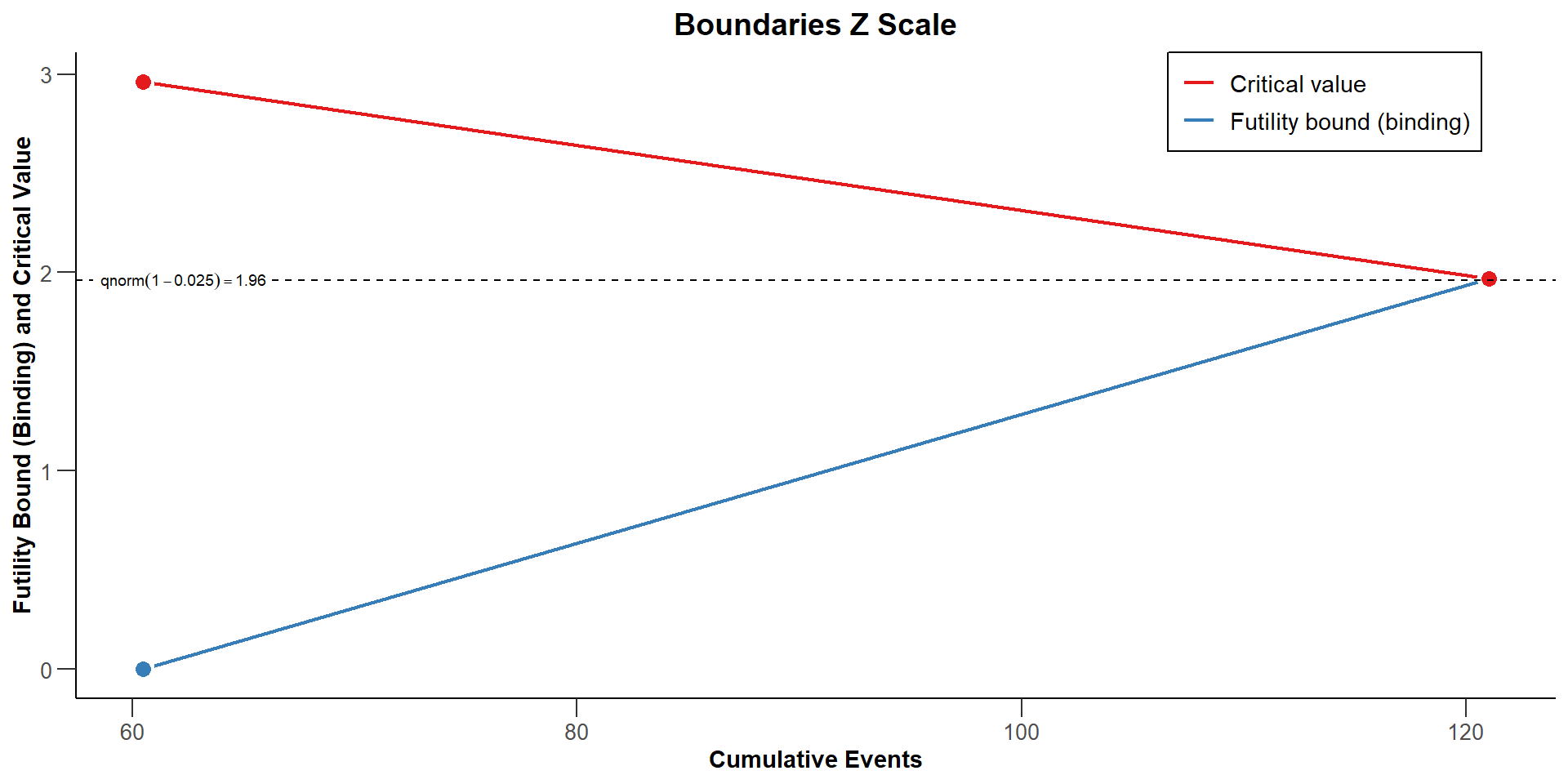
$`Boundaries Effect Scale`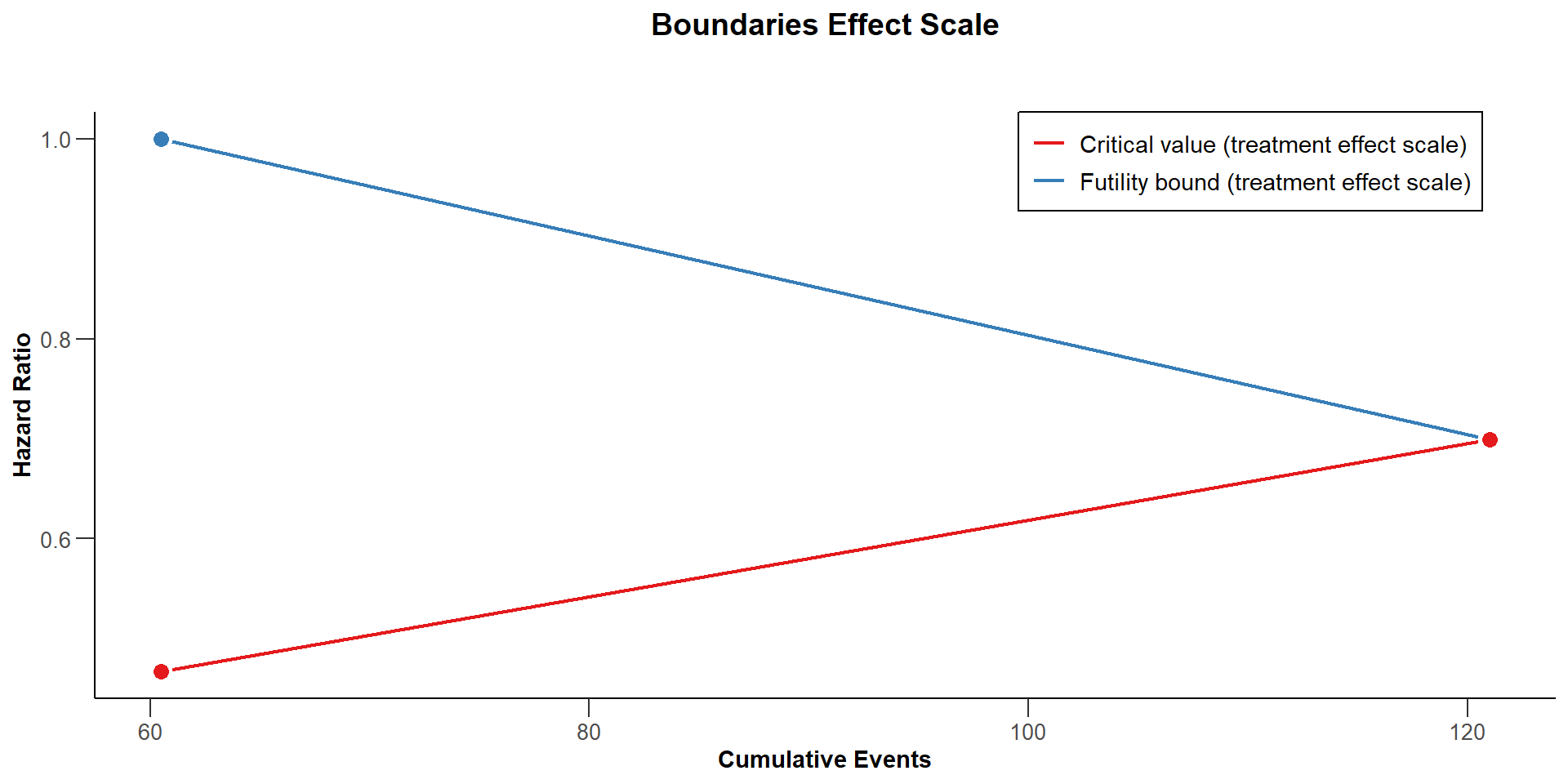
$`Boundaries p Values Scale`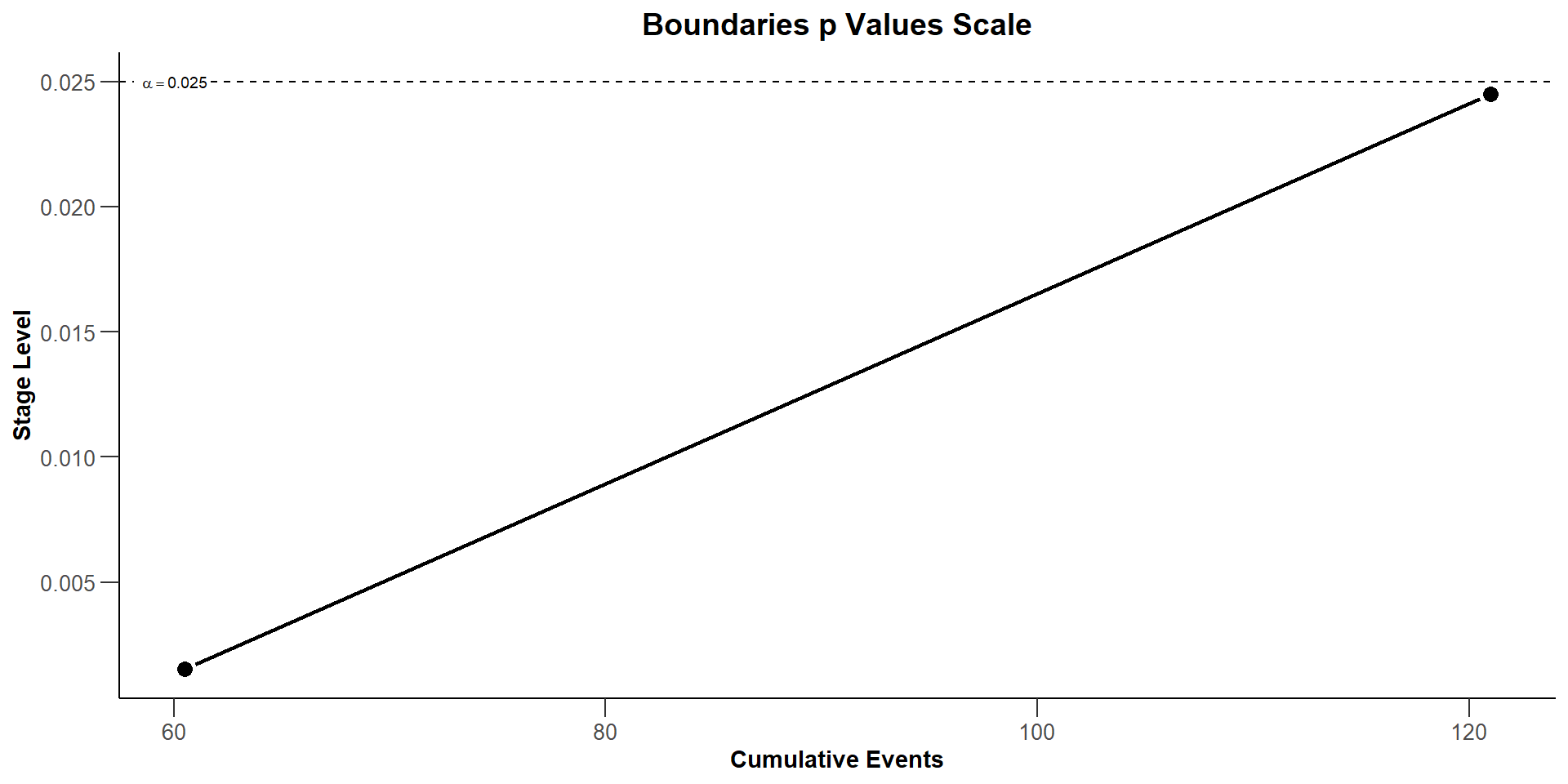
$`Error Spending`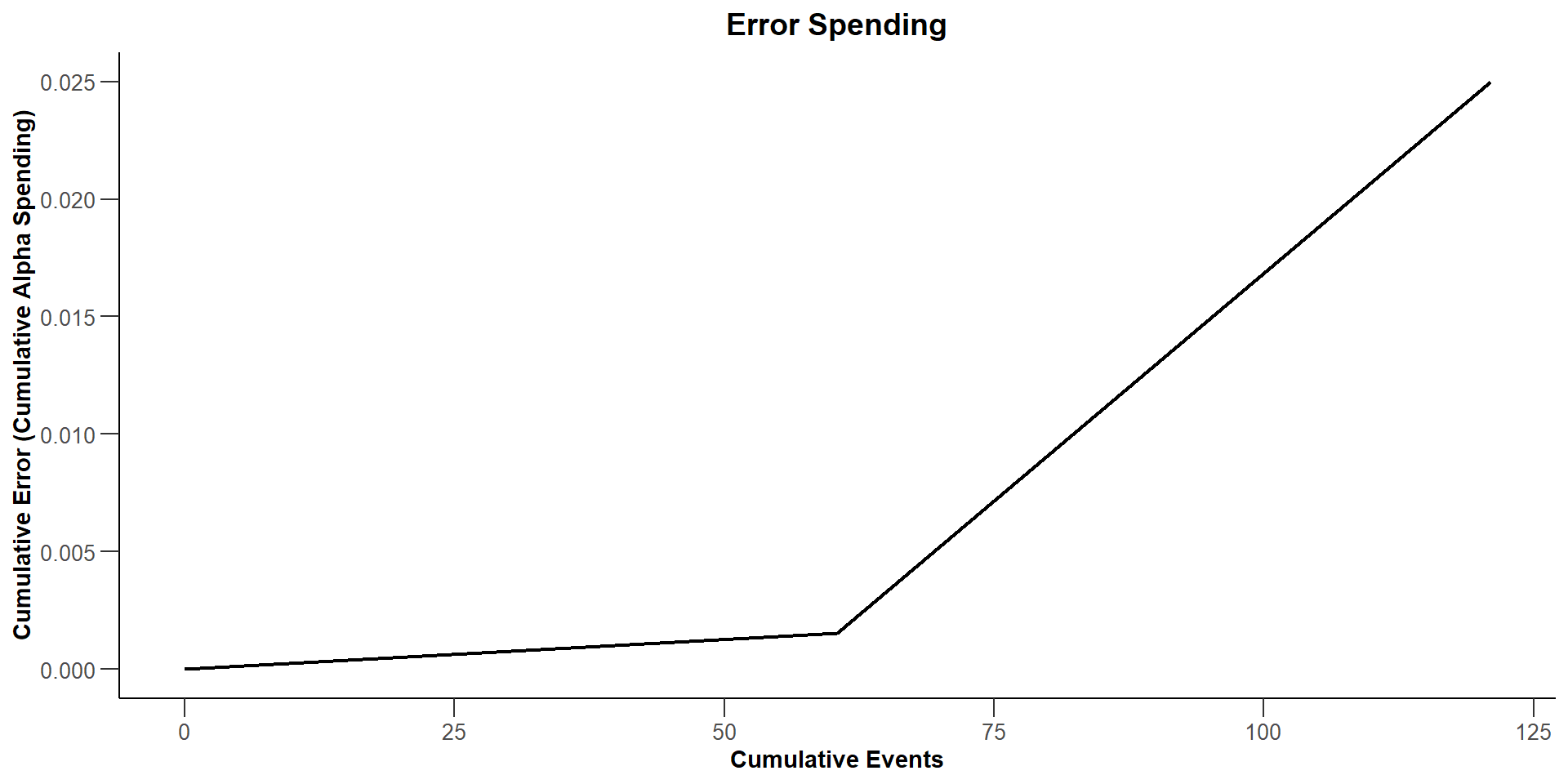
$`Overall Power and Early Stopping`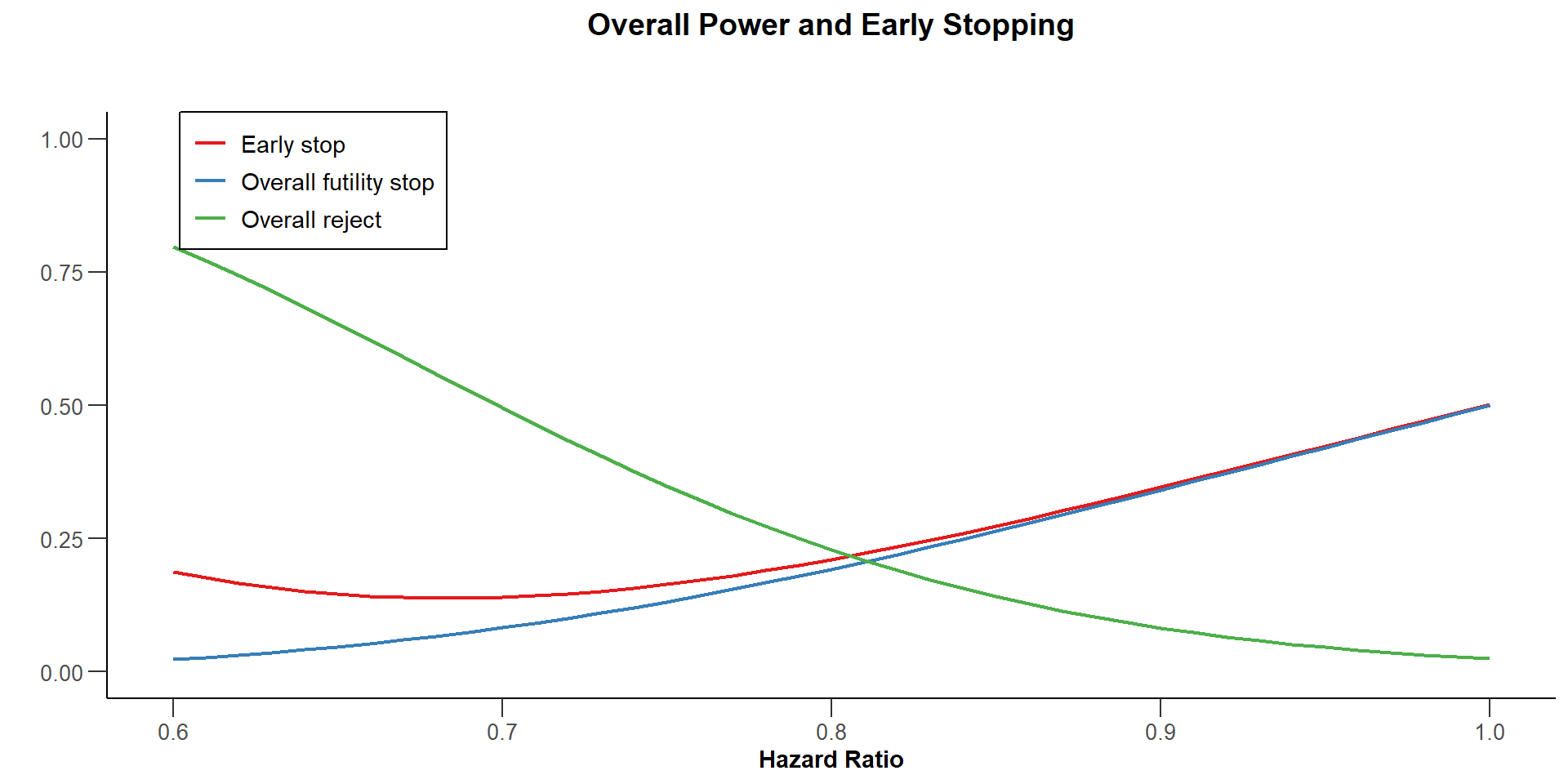
$`Number of Events`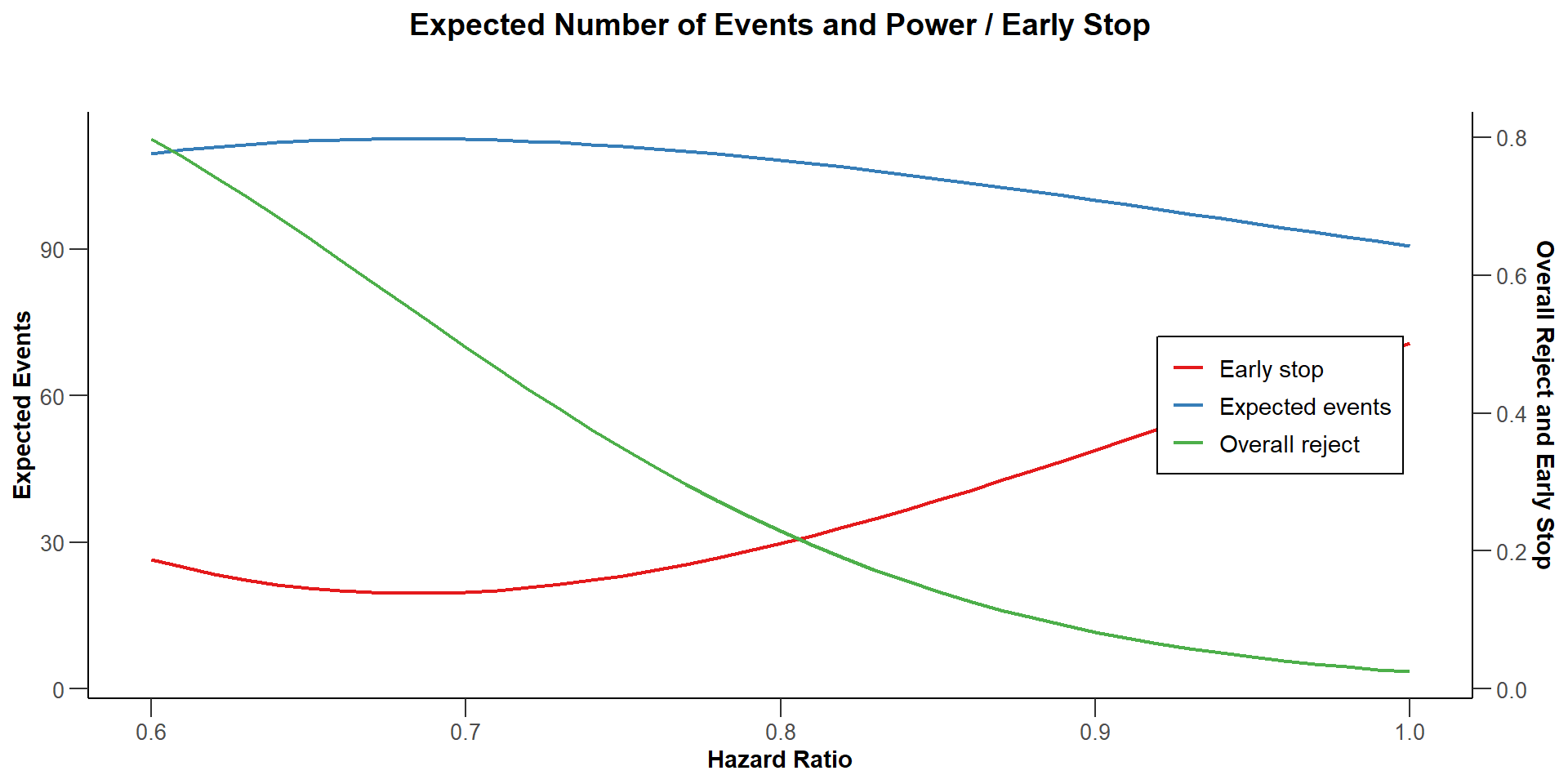
$`Overall Power`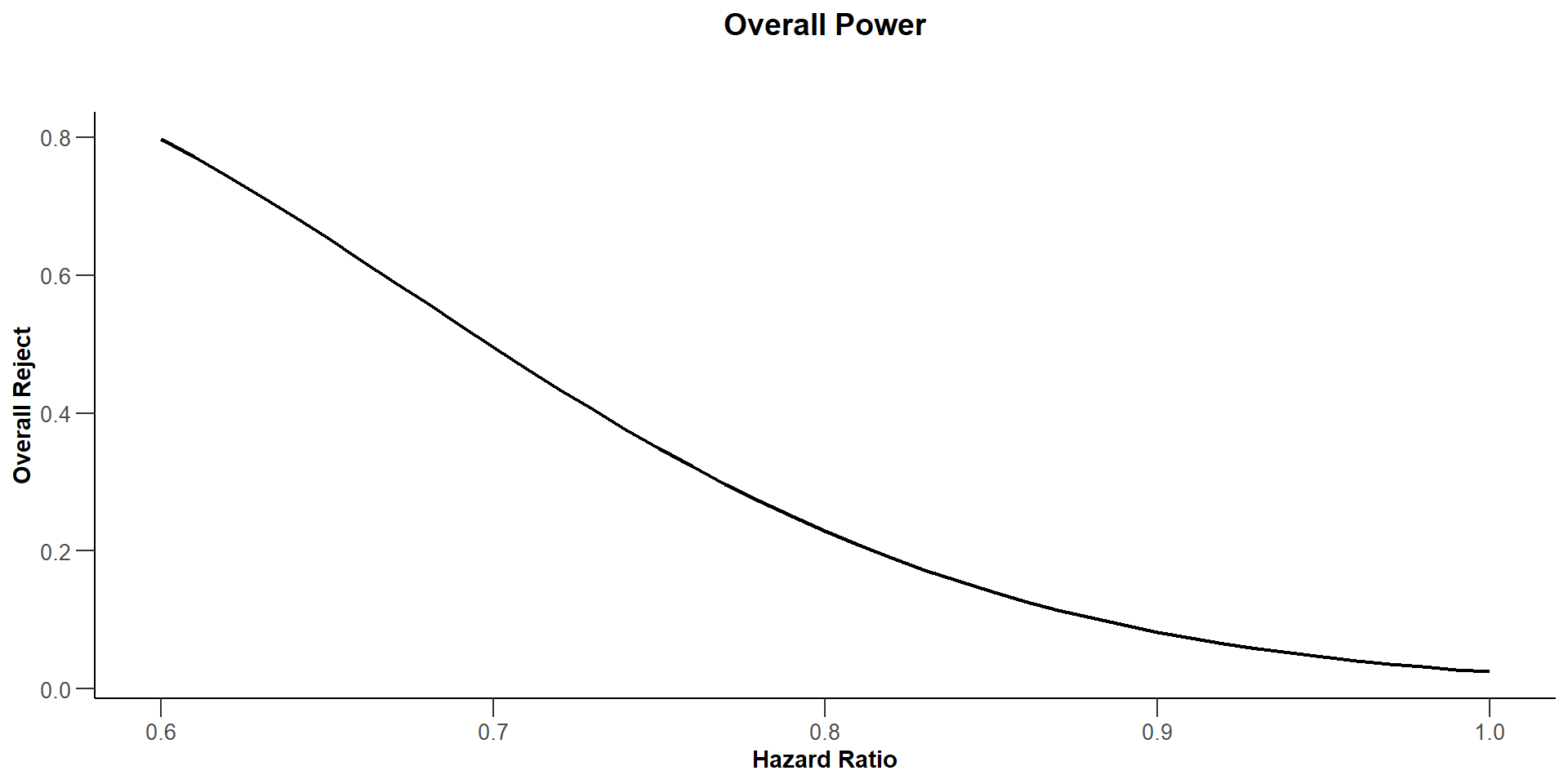
$`Overall Early Stopping`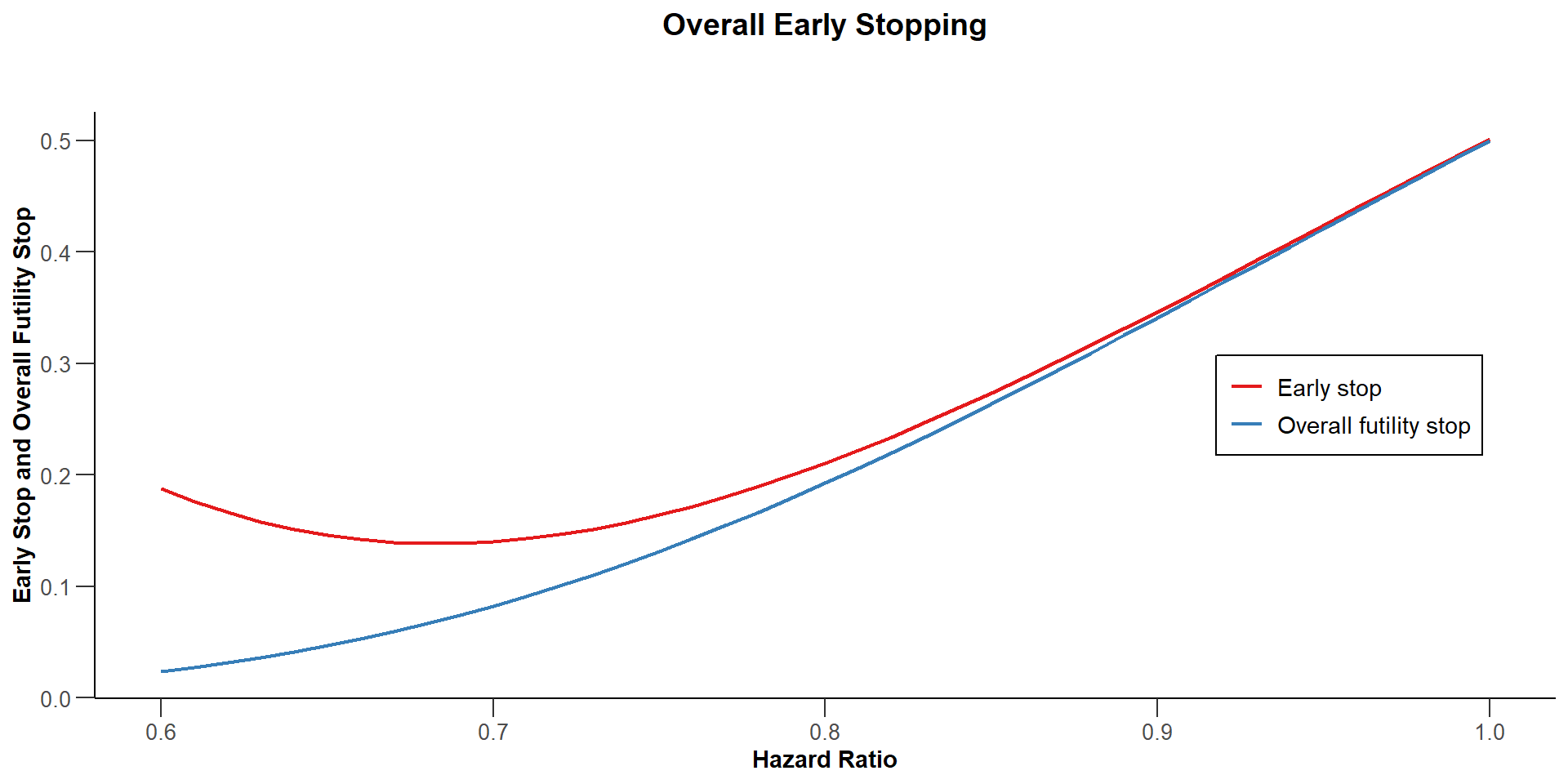
$`Expected Number of Events`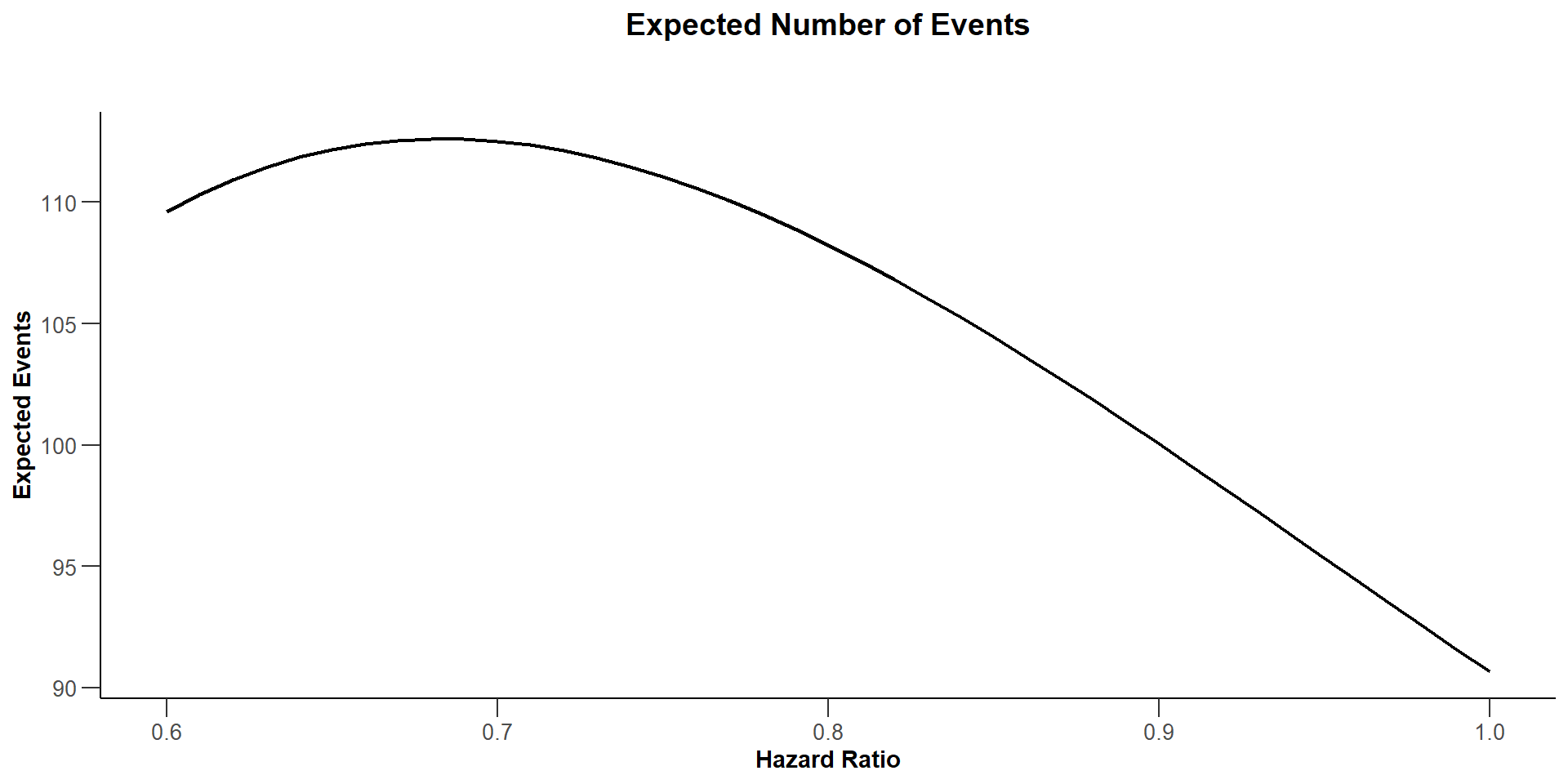
$`Study Duration`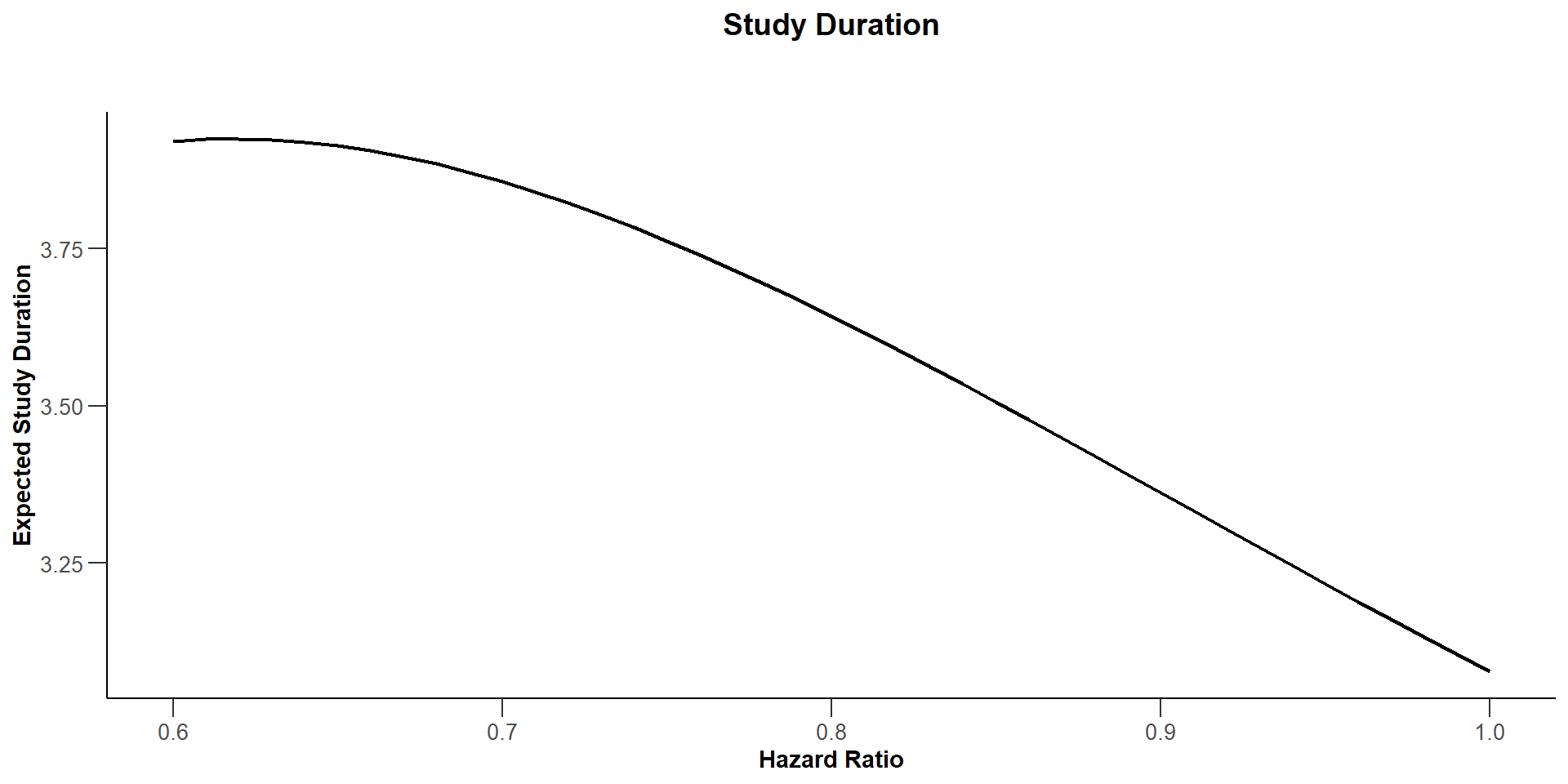
$`Expected Number of Subjects`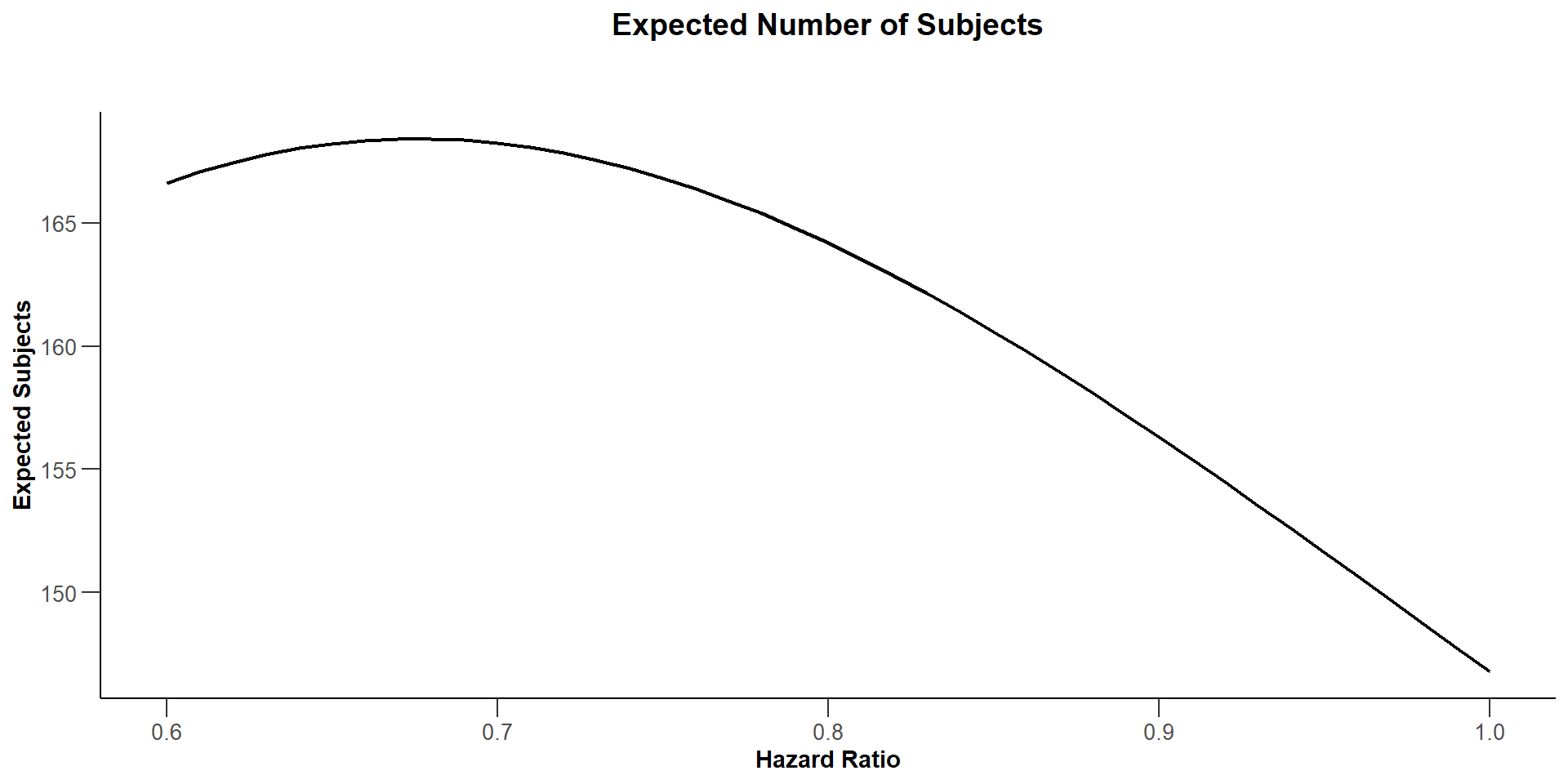
$`Analysis Time`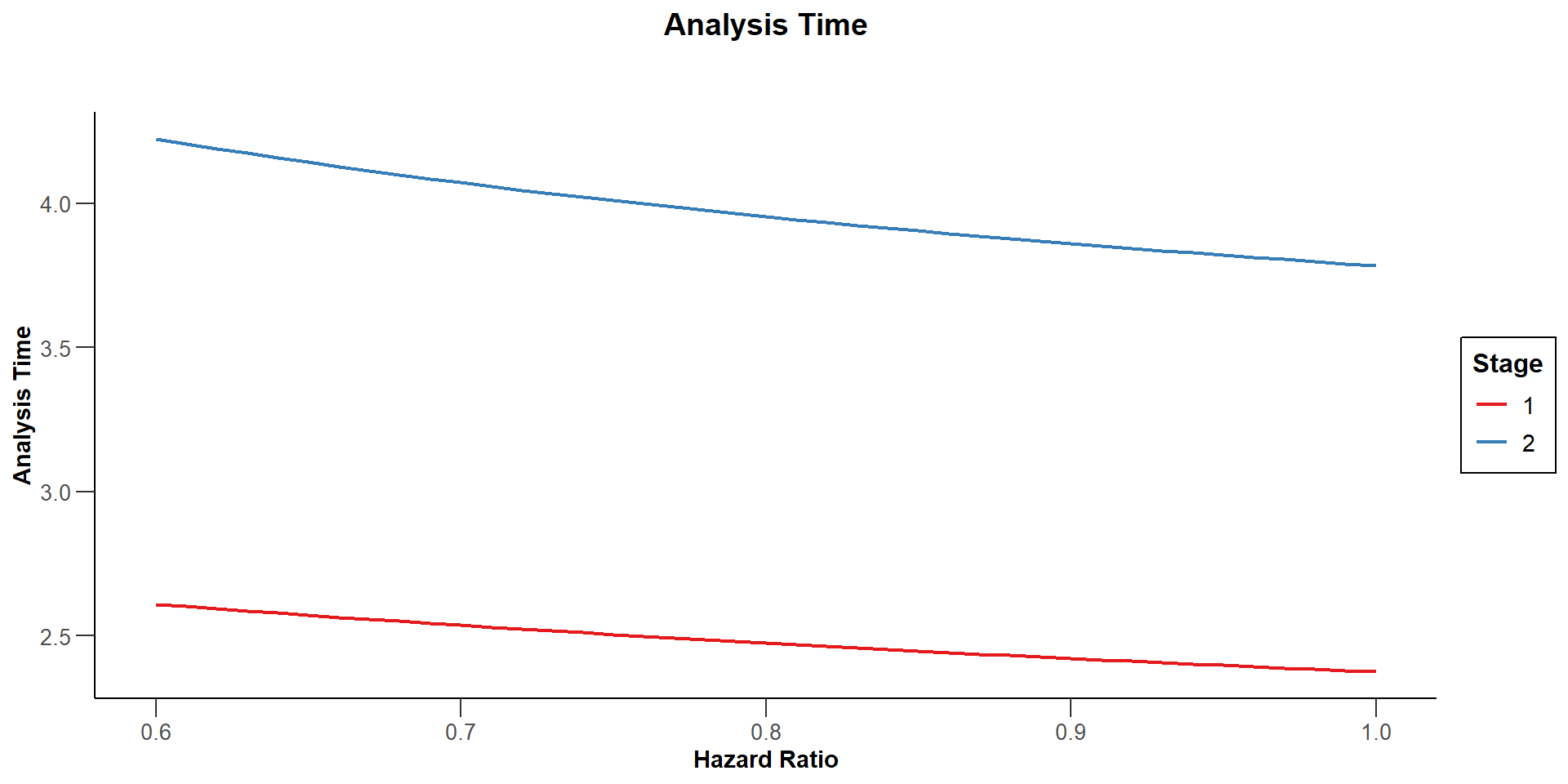
$`Cumulative Distribution Function`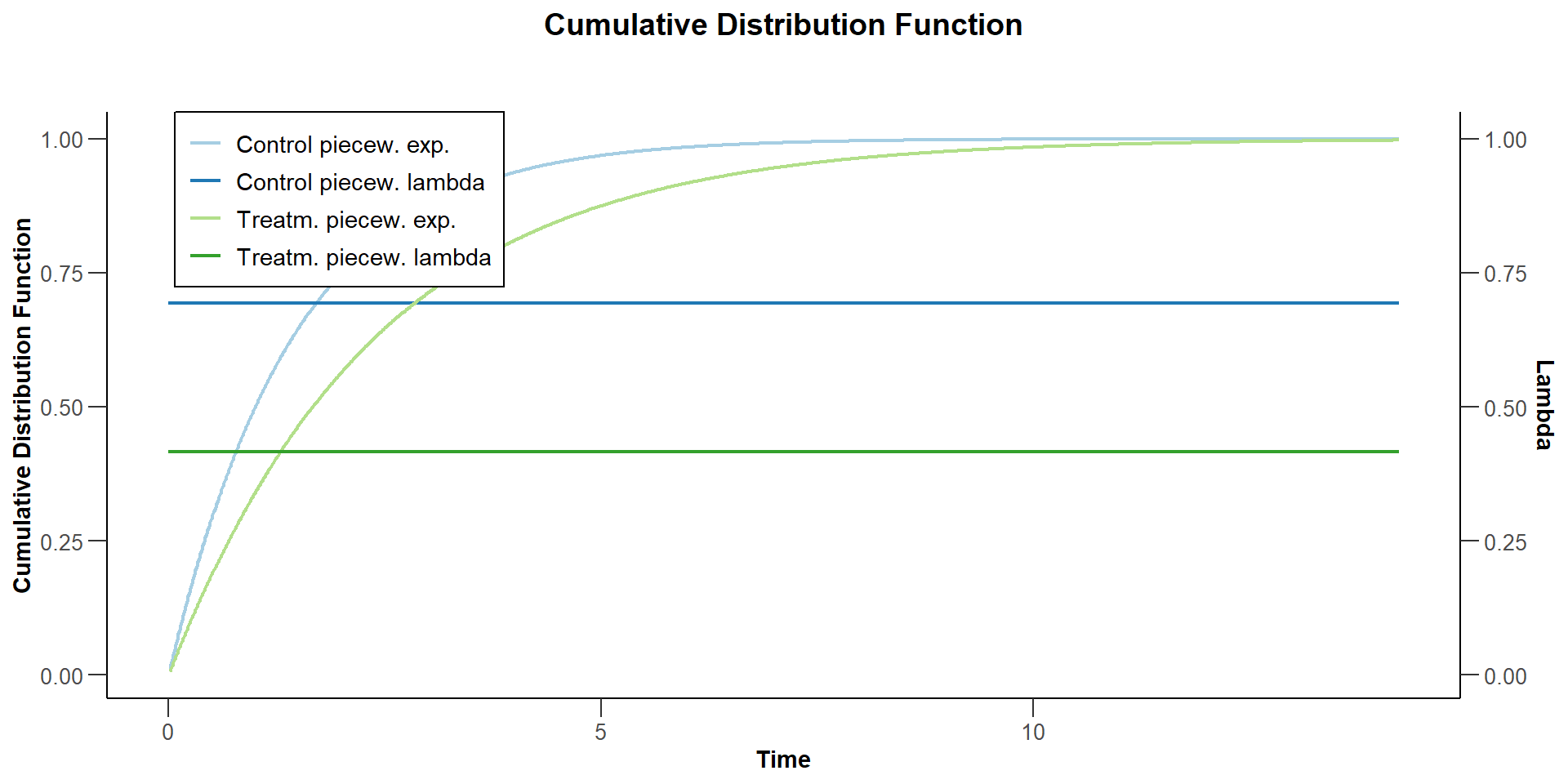
$`Survival Function`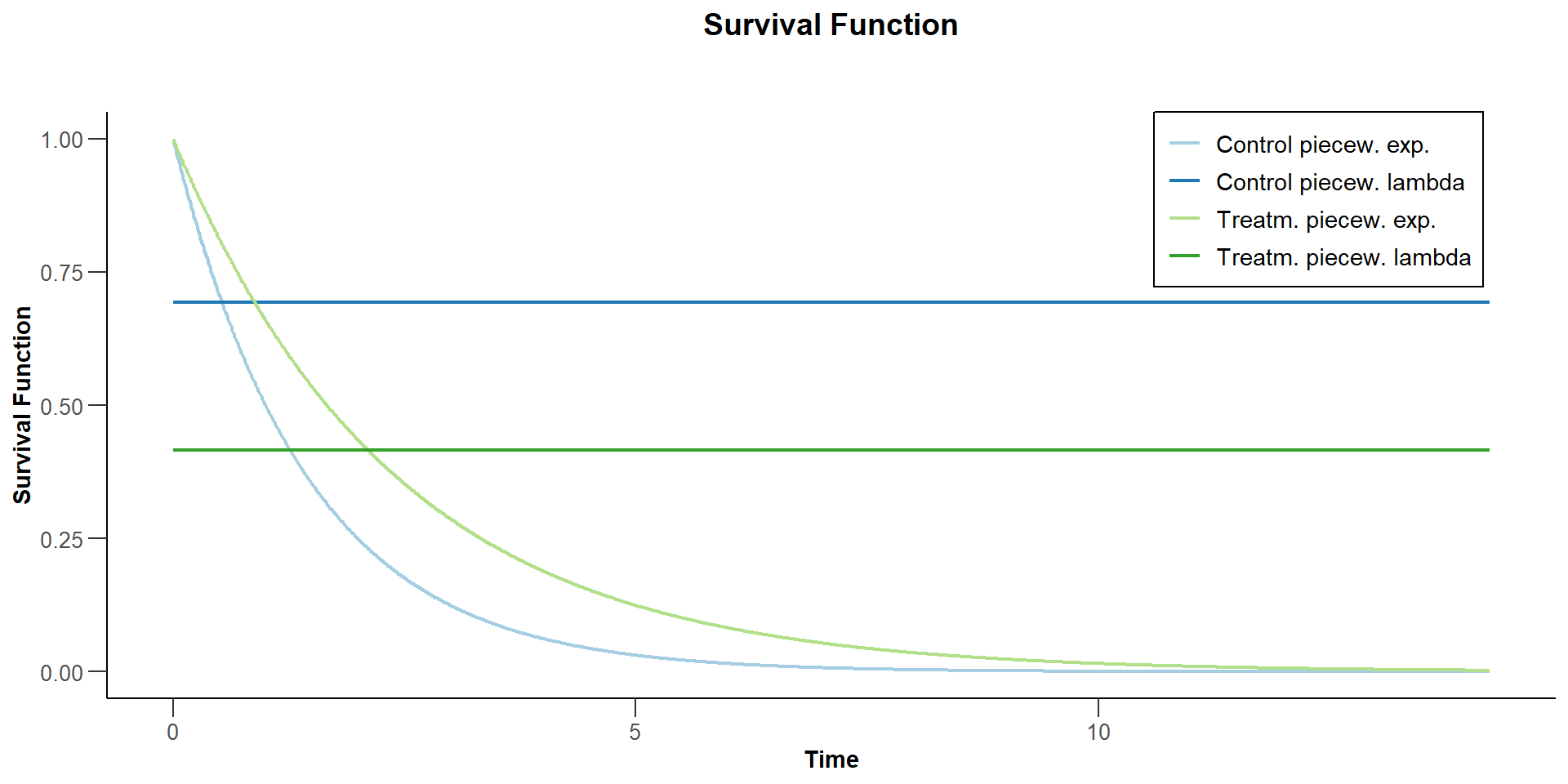
Survival Analysis
Interim Analysis Stage
Suppose at the interim analysis, the observed number of events is 67 and the value of the Z-statistic is -1.10 (where negative values correspond to treatment benefit).
Question 7
Re-calculate the stopping boundary based on the observed 67 events at the interim analysis.
- Assume the same alpha-spending function as above.
- Assume the planned maximum number of events is 121.
What is the interim analysis decision?
Test decision
Continue to the next stage, since the Z statistic is between 0 (futility bound) and -2.795 (efficacy bound)
\(\hspace{2cm}\)
Direction of test statistic
NOTE: The function getDesignGroupSequential() doesn’t know which direction of Z statistic indicates treatment benefit. By default, the critical values are displayed assuming positive Z is beneficial.
Final Analysis Stage
Suppose at the final analysis, the observed number of events is 129 and the value of the Z-statistic is -2.00 (where negative values correspond to treatment benefit).
Question 8
Re-calculate the stopping boundary based on the observed 67 events at interim and 129 events at the final analysis.
Since we have deviated from the planned maximum number of events (= 121), our actual alpha spent no longer follows the O’Brien-Fleming-type alpha-spending function. Use the argument typeOfDesign = "asUser" instead.
getDesignGroupSequential(
typeOfDesign = "asOF",
informationRates = c(67 / 121, 1),
alpha = 0.025
) |> fetch(alphaSpent)$alphaSpent
[1] 0.002594128 0.024999990Final test decision
Reject the null hypothesis since Z < -1.9764
Alternative
Use maxInformation and getAnalysisResults()
# Dummy design
designDummy <- getDesignGroupSequential(
typeOfDesign = "asOF",
directionUpper = FALSE
)
dataExample <- getDataset(
cumEvents = 67,
cumLogRanks = c(-1.10)
)
getAnalysisResults(
design = designDummy,
dataInput = dataExample,
maxInformation = 121
) |> summary()Analysis results for a survival endpoint
Sequential analysis with 2 looks (group sequential design), one-sided overall significance level 2.5%. The results were calculated using a two-sample logrank test. H0: hazard ratio = 1 against H1: hazard ratio < 1.
| Stage | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Planned information rate | 55.4% | 100% |
| Cumulative alpha spent | 0.0026 | 0.0250 |
| Stage levels (one-sided) | 0.0026 | 0.0242 |
| Efficacy boundary (z-value scale) | 2.795 | 1.974 |
| Cumulative effect size | 0.764 | |
| Overall test statistic | -1.100 | |
| Overall p-value | 0.1357 | |
| Test action | continue | |
| Conditional rejection probability | 0.0418 | |
| 95% repeated confidence interval | [0.386; 1.513] | |
| Repeated p-value | 0.2669 |
Second stage
dataExample <- getDataset(
cumEvents = c(67, 129),
cumLogRanks = c(-1.10, -2.0)
)
getAnalysisResults(
design = designDummy,
dataInput = dataExample,
maxInformation = 121
) |> summary()Analysis results for a survival endpoint
Sequential analysis with 2 looks (group sequential design), one-sided overall significance level 2.5%. The results were calculated using a two-sample logrank test. H0: hazard ratio = 1 against H1: hazard ratio < 1.
| Stage | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Planned information rate | 51.9% | 100% |
| Cumulative alpha spent | 0.0026 | 0.0250 |
| Stage levels (one-sided) | 0.0026 | 0.0241 |
| Efficacy boundary (z-value scale) | 2.795 | 1.976 |
| Cumulative effect size | 0.764 | 0.703 |
| Overall test statistic | -1.100 | -2.000 |
| Overall p-value | 0.1357 | 0.0228 |
| Test action | continue | reject |
| Conditional rejection probability | 0.0439 | |
| 95% repeated confidence interval | [0.386; 1.513] | [0.496; 0.996] |
| Repeated p-value | 0.2669 | |
| Final p-value | 0.0237 | |
| Final confidence interval | [0.498; 0.996] | |
| Median unbiased estimate | 0.704 |
Extensions
Drop-outs
Question 9
Going back to the assumptions in Question 3, what is the expected study duration for a fixed sample size design if we specify in addition that 2% of subjects on each arm will drop out per year?
Was 4.776 without dropouts
Staggered Patient Entry
Question 10
Suppose the patient entry is not uniform, but staggered in intervals. For example, the accrual starts with 30 patients in the first year, 40 in the second, and 50 in the third.
What is the expected study duration (under H1)?
Was 4.984 with uniform patient entry
Note
We have to increase the accrual time because otherwise #events > #patients
getSampleSizeSurvival(
alpha = 0.025,
beta = 0.2,
median2 = 1,
hazardRatio = 0.6,
accrualTime = c(0, 1, 2, 3.5),
accrualIntensity = c(30, 40, 50),
dropoutRate1 = 0.02,
dropoutRate2 = 0.02,
dropoutTime = 1,
allocationRatioPlanned = 1
) |> summary()Sample size calculation for a survival endpoint
Fixed sample analysis, one-sided significance level 2.5%, power 80%. The results were calculated for a two-sample logrank test, H0: hazard ratio = 1, H1: hazard ratio = 0.6, control median(2) = 1, accrual time = c(1, 2, 3.5), accrual intensity = c(30, 40, 50), dropout rate(1) = 0.02, dropout rate(2) = 0.02, dropout time = 1.
| Stage | Fixed |
|---|---|
| Stage level (one-sided) | 0.0250 |
| Efficacy boundary (z-value scale) | 1.960 |
| Efficacy boundary (t) | 0.700 |
| Number of subjects | 145.0 |
| Number of events | 120.3 |
| Analysis time | 5.83 |
| Expected study duration under H1 | 5.83 |
Legend:
- (t): treatment effect scale
More Complicated Survival Distributions
Suppose now that the control arm follows a piecewise exponential distribution. For the first year the hazard rate is log(2) / 1 = 0.693, and thereafter the hazard rate is 0.5.
Question 11
What is the expected study duration?
Was 5.83 with constant hazard rate
Non-Proportional Hazards
Suppose that, in addition to the changing hazard rate on the control arm, the hazard ratio also changes.
Suppose that the hazard ratio during the first year is 0.6. Thereafter, the hazard ratio is 0.8.
Question 11
Use the function getSimulationSurvival() to calculate the power of the fixed sample size design with 3.5 years recruitment (50 subjects per year).
tictoc::tic()
getSimulationSurvival(
piecewiseSurvivalTime = c(0, 1),
lambda2 = c(0.693, 0.5),
hazardRatio = c(0.6, 0.8),
directionUpper = FALSE,
plannedEvents = 121,
accrualTime = c(0, 3.5),
accrualIntensity = 50,
maxNumberOfIterations = 10000
) |> fetch(overallReject)overallReject
0.5766 0.8 sec elapsedSummary
- Introduction to design and analysis of survival design
- For survival designs, many additional options for specifying patient recruitment, survival time distribution, and effect size pattern available
- Flexible trial conduct through use of \(\alpha\)-spending approach
- Caveat: No data-driven reassessment of information possible without jeopardizing Type I error control
- Alternative: p-value combination approach: use of inverse normal combination of Fisher’s combination test
- Application, e.g., within promizing zone design, see Vignette Promizing Zone Design with rpact
- Use of fast and flexible
getSimulationSurvival()function for assessing these designs
Questions??
